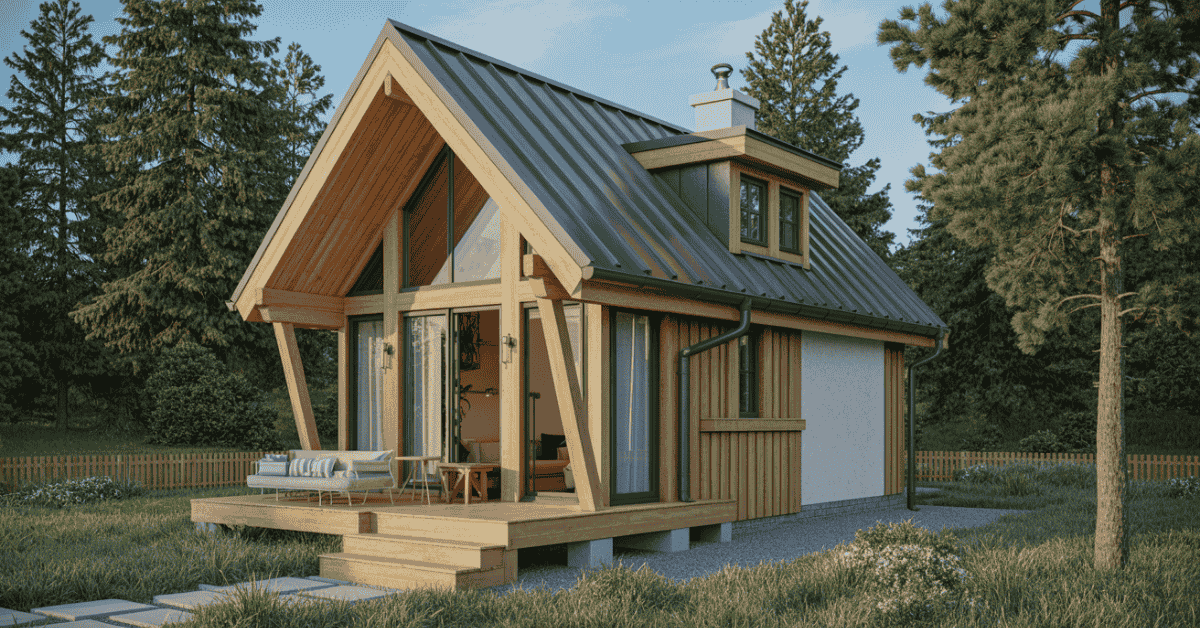
Nearly 100 tiny house plans are available online, priced from $129 to $490. This shows that building a small wooden home is now possible for many.
This guide provides a straightforward, seven-step process for building a small wooden house. You’ll have access to plans created by experienced designers. These include the Backyard Studio Kenzo, Small Round Cabin Olivia, and A-Frame Weekender.
These plans come with detailed measurements, foundation info, and a full list of materials. This makes building a tiny wooden house easier.
You’ll find clear instructions for framing, roof cuts, and finishing. These plans are budget-friendly, making it possible for both weekend builders and serious DIYers to start their project.
Key Takeaways
- Marketplaces list roughly 99 tiny house plans with prices typically between $129 and $490.
- Professional plans often include both metric and imperial measurements and full materials lists.
- The seven-step tutorial breaks down the project into manageable phases for DIY builders.
- Popular plan types include backyard studios, round cabins, A-frames, and portable cabins.
- Designer-backed blueprints reduce guesswork and help control costs for a diy tiny wooden house.
Why Choose Small Wooden Houses: Benefits of Tiny House Plans and DIY Cabin Plans
Small wooden houses are great for saving money and keeping things simple. They use less material and labor. Many builders choose plans that list everything needed to stay on budget and reduce waste.
Designing small saves money. They need less foundation, HVAC, and cladding. Some tiny house plans are cheap and can be built quickly. DIY cabin plans let homeowners save on contractor costs by doing the work themselves.
Keeping a small house in good shape is easy. They have fewer surfaces to fix and use less energy. Experienced designers make layouts that are efficient and comfortable. This means less money spent on repairs and utilities over time.
Small houses are also good for the planet. They use less lumber, have smaller appliances, and can be off-grid. They are easy to move and have a small environmental impact. Many builders choose them for these reasons.
Small houses fit many lifestyles. They can be a weekend getaway or a full-time home. They are versatile and can be used in different ways.
Plans often include features like porches and lofts. They have detailed material lists and modular designs. This makes building faster and reduces waste. It’s why many people choose small house plans, whether they build it themselves or buy a kit.
| Benefit | How Plans Help | Best Fit |
|---|---|---|
| Lower build cost | Reduced materials, smaller foundations, clear material lists | Budget builds, first-time owners |
| Faster build time | Modular details, transportable options, skids or piers | Weekend cabins, backyard studios |
| Lower maintenance | Simpler systems, compact footprints, efficient layouts | Retirees, minimalists |
| Environmental impact | Less waste, off-grid choices, smaller energy use | Eco-conscious owners |
| Flexibility | Designs for lofts, porches, and multi-use spaces | Full-time tiny homes, part-time retreats |
Planning Your Project: Selecting the Right Small Wooden Houses Plans DIY

Choosing the right plan makes building easier and avoids surprises. First, think about how you’ll use the structure. Will it be a weekend cabin, a backyard studio, or a tiny home? This helps narrow down options like compact cabins, cozy cottages, A-frames, or mobile homes.
How to choose between cabin, cottage, A-frame, and transportable designs
Consider your site and lifestyle needs. An A-frame is great for steep lots and sheds snow. A small round cabin can add modern flair to wooded areas. Wooden cottages with porches are perfect for flat rural plots, offering classic charm. Transportable homes are ideal for those who need to move or have minimal site prep.
Designers like Tiny Heirloom and New Frontier offer plans for each style. Look at square footage, roof pitch, insulation, and price. Match these to your needs and budget.
Considering local zoning, building approvals, and foundation types
Check local codes early. Some places don’t require full permits for structures on skids or trailers. Others need standard foundations and inspections. Know the size limits, setback rules, and utility hookups before buying plans.
Many tiny house plans work with skids, piers, or slab foundations. Choosing a plan with flexible foundation notes saves time. If you plan to stay, prepare for full code compliance and engineer-stamped details.
Using professional plans versus custom or prefab options
Professional plans from firms like Tiny Heirloom include detailed materials lists and builder notes. These details help with procurement and reduce risk during construction.
Custom plans let you match your site and style, but they cost more and take longer. Prefab or panelized options save on labor and cutting, but are pricier. Consider your carpentry skills, local codes, and budget when choosing DIY plans, custom architecture, or prefab kits.
Design Essentials: Small Wooden Cabin Designs and Wooden Cottage Plans

Good design starts with a clear plan that matches site, budget, and use. Many small wooden cabin designs and wooden cottage plans include lofts and porches. These features expand living space without growing the footprint. Thoughtful layouts make a tiny living feel open and flexible.
Layout ideas: lofts, porches, and multi-use spaces
Lofts add a sleeping area while freeing the main floor for living and kitchen functions. A-frame loft plans use angled roofs to frame a cozy upper bed area. Porches extend usable space outdoors and improve curb appeal for cottage-style plans.
Multi-use zones let one room serve as dining, work, and guest space. Built-in storage under stairs and bench seating keep clutter low. Clear circulation paths make small floor plans practical and pleasant.
Materials and finishes for rustic tiny house plans and modern alternatives
Rustic tiny house plans often specify cedar or pine siding with walnut stain for warmth and durability. Modern variants favour steel, fibre-cement, or vertical cedar for a sleeker look. Detailed wooden cottage plans include material lists to help pick finishes suited to the local climate.
Designers balance cost and longevity by recommending treated lumber for decks and rot-resistant trim around windows. Roof choices range from asphalt shingles to metal standing seam, depending on budget and desired lifespan.
Energy-efficient choices and off-grid design considerations
Insulation, airtight windows, and correct orientation improve year-round comfort and lower energy needs. Passive solar siting places living spaces to the south in the Northern Hemisphere. Off-grid buyers find that many diy tiny house plans and off-grid kits include guidance on panels, batteries, and propane or wood heat systems.
Simple measures such as triple-seal doors, R-30 roof insulation, and a small heat-recovery ventilator add efficiency without large cost increases. For remote builds, choose durable exterior finishes and easy-service mechanicals.
| Design Element | Benefit | Typical Materials |
|---|---|---|
| Loft sleeping area | Increases sleeping capacity without larger footprint | Light timber framing, ladder or compact stair |
| Front porch | Outdoor living, weather buffer for entry | Cedar decking, pressure-treated joists, composite railing |
| Rustic finishes | Warm, traditional aesthetic | Pine or cedar siding, walnut stain, shale or cedar roof |
| Modern alternatives | Low maintenance, contemporary look | Increases sleeping capacity without a larger footprint |
| Energy efficiency | Lower energy bills and better comfort | High-R insulation, double/triple-pane windows, HRV |
| Off-grid readiness | Independent operation in remote sites | Solar array, battery bank, propane or wood stove backup |
Preparing Materials and Tools: Woodworking House Building Plans and Easy DIY Woodworking Projects
Begin by carefully reviewing your chosen plans. Professional woodworking house building plans include precise measurements in both metric and imperial units. They detail lumber, fasteners, roofing, insulation, doors, windows, and finishing materials. Buying a full set of plans, priced between $129 and $490, helps budget a small wooden house.
Before making the first cut, order or mark all materials. Many builders suggest pre-cutting and numbering pieces to speed up assembly. For easy DIY woodworking projects, label each board and keep a simple staging area for components. Use clamps and wood glue for joins in models, then scale up with full-size fasteners for the cabin.
Choose the right tools for the job. A compact list saves trips and keeps costs low. Essential tools include a circular saw, miter saw, drill/driver, framing nailer, levels, chisels, and safety gear. For specialised tasks, add a router, a jigsaw, and a padsaw for kerfs on trim work. These tools cover most tasks in wooden house design DIY efforts.
Plan the complete materials list from foundation to finish. Plans with full materials lists reduce waste and unexpected purchases. Typical items include foundation blocks or skids, wall studs, sheathing, roofing underlayment, shingles or metal roofing, insulation batts, exterior siding, interior drywall or panelling, doors, windows, trim, and fasteners.
Use a simple budgeting method. Compare plan prices and factor in materials, tools, and rental costs for speciality equipment. Buying lumber from Home Depot or Lowe’s is convenient. Local sawmills can offer savings on framing lumber. Reclaimed timbers add character and can lower costs if you account for extra labor in preparation.
Plan for small hardware and finish items. Hinges, latches, weatherstripping, screws, nails, and sealants add up. Buy these in bulk where possible. For easy DIY woodworking projects, a well-stocked hardware kit prevents downtime and keeps momentum on site.
Scale model tips to full builds. Use clamps, wood glue, and temporary fasteners during dry fits. When ready to final-assemble, switch to structural screws and nails recommended by the plan. Keep a clear cutting list and follow manufacturer recommendations for engineered products like I-joists or SIPs in more advanced wooden house design DIY schemes.
Use the table below to compare common material sources, typical savings, and recommended items to buy first. This helps align project rhythm with supply availability and budget targets for small wooden houses plans DIY.
| Source | Typical Strengths | Estimated Savings | Recommended First Purchases |
|---|---|---|---|
| Home Depot / Lowe’s | Dimensional lumber, plywood, screws, and basic tools | 0–10% on retail pricing with promotions | Complete materials lists, cut lists, and hardware specs |
| Local Sawmill | Custom cuts, nominal lumber at lower cost | 10–25% vs. big-box on bulk orders | Framing studs, beams, rough-sawn siding |
| Reclaimed Materials | Unique character, eco-friendly | Up to 50% if labor is affordable | Timber, flooring, decorative trim |
| Specialty Vendors (Windows, SIPs) | Higher performance, engineered components | Varies; value in time saved and energy efficiency | Windows, doors, insulation panels |
| Online Plan Sellers | Detailed lists, metric/imperial measurements | Predictable budgeting; plan prices $129–$490 | Complete materials lists, cut lists, hardware specs |
Build Small Wooden House Step by Step: The 7-Step Construction Overview

This seven-step guide helps turn plans into a real tiny home. It works with both DIY and professional blueprints. It breaks down big tasks into smaller steps, making it easier for everyone to plan.
Step 1: foundation and site setup. First, mark the area and level it. Then, install the foundation, like piers or a slab. This step is crucial for avoiding mistakes later.
Step 2: framing. Next, build the wall and roof frames using pre-cut pieces. Following your plans closely helps avoid errors.
Step 3: Roofing. Now, put on the roof’s sheathing, underlayment, and finish. Make sure to reinforce the roof to prevent leaks.
Step 4: Exterior cladding and weatherproofing. Add siding, flashing, and trim. This step helps protect the house from the weather.
Step 5: Doors, windows, and stairs. Install these according to the manufacturer’s instructions. This ensures everything fits right.
Step 6: Interior finishes and systems. Run the electrical and plumbing, then insulate and finish the walls. If needed, hire pros for safety and permits.
Step 7: Final trim and inspection. Finish with trim, stain, and hardware. Do a final check before moving in.
Building time and crew size vary. A prefab kit can be set up quickly by a few people. DIY builds take longer, depending on the project’s size and your experience. Prefab kits are good for speed, while custom builds are better for unique sites.
Common mistakes and how to fix them:
- Inaccurate cuts — double-check measurements and use jigs for accuracy.
- Misaligned joints — test assemblies before securing them.
- Inadequate roof bracing — add extra support and follow the plan’s spacing.
- Moisture control failures — use proper flashing and ventilation to protect the house.
Experienced designers suggest a clear plan and labelling. Follow these steps to build a wooden house. Use reliable plans and get help for tricky parts.
Foundations and Structural Work: How to Build a Small Wooden House Safely

Choosing the right base is crucial for a tiny house. Plans often suggest skids for easy transport, concrete piers for uneven ground, and more. Each choice affects how the house will be used and how long it will last.
Comparing foundation types
Skids make a cabin easy to move and save on-site work. Piers need less digging and let air under the floor. Raised foundations keep the house dry and warm. Simple slabs are quick and easy on stable ground.
Architects often list foundation parts and how they affect the frame. Always check local building codes before starting.
Framing tips for lasting structure
Begin with a level sill plate and use treated lumber where it touches concrete. Accurate layout is key; use a square and story pole for consistent cuts. Builders suggest adding collar ties and connectors at roof corners to fight wind.
Mark and test-fit angled rafters before cutting many. A 30° angle on both sides makes joining easier. Add bracing at corners to prevent wall movement during roofing.
Anchoring, insulation, and moisture control
Anchoring keeps cabins stable in storms and meets building codes. Use bolts on slabs and straps on piers and skids. For mobile homes, straps and trailer mounts are essential.
Start moisture control with good flashing at the roof and window edges. Overhangs keep rain off walls and protect the foundation. Use a vapour barrier in crawlspaces and choose insulation based on your climate.
| Foundation Type | Best Use | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Skids | Transportable cabins, seasonal units | Low site work, portable, fast setup | Limited permanence, less frost protection |
| Piers | Uneven terrain, minimal excavation | Cost-effective, good airflow, adaptable | Requires anchoring, potential cold floor |
| Raised foundation | Flood-prone sites, improved crawlspace | Better insulation access, moisture separation | Higher material and labour costs |
| Concrete slab | Stable, level sites; permanent builds | Low maintenance, strong load distribution | More excavation, less mobility, frost issues |
Detail Work: Doors, Windows, Roofs, and Interior Finishes for DIY Tiny House Plans
Building a tiny house requires attention to detail. When installing doors and windows, focus on fit, weatherproofing, and hardware. Good plans help by listing the necessary materials from trusted suppliers like Simpson Strong-Tie and National Hardware.
Door and frame integration
Start by cutting logs or timbers for true door openings. Ensure the door sizes match the openings. Use hinges and set them so doors close fully without sticking.
Add a small floor platform inside where doors open. This makes the threshold usable and keeps out cold drafts.
Window fit and sealing
Position windows for the right balance of light and privacy. Use prefinished units for consistent performance. Seal the jambs with flashing and foam.
Check that doors and windows work smoothly after adding walls and trim.
Roof assembly tips
Mark angle cuts before cutting rafters for a clean ridge. Use internal logs or collar ties to strengthen the roof. Apply sheathing made from glued wood sticks or plywood/OSB.
Fastening and weather control
Use corrosion-resistant fasteners and apply weatherproof flashing. Seal the ridge and eave details to keep out rain. Slate or composite shingles can mimic the model’s look.
Interior finishes and circulation
Choose flooring based on use: hardwood for warmth, engineered floors for stability. Prefabricated stairs save time. Trim, stain, or paint should match the plan’s aesthetic.
Professional plans include interior finishes with recommended materials and suppliers.
Small-scale lessons for full-size builds
Apply model accuracy to real-world checks: verify door clearances, test hinge loads, and confirm rafter angles. Keep a hardware list and follow supplier recommendations. These steps reduce rework and ensure the final tiny home delivers function and charm.
Affordable Small House Plans: Sourcing Plans, Kits, and Professional Support
Finding the right plans is key to keeping costs down and projects successful. Online marketplaces and speciality stores offer a wide range of designs. Prices for tiny house plans vary from $129 to $490, including detailed materials lists.
Choosing where to buy tiny house plans depends on what you need. Digital platforms like Etsy and niche websites have many styles. Established designers and firms provide plans with buildability notes and community support, helping avoid construction surprises.
Plans with detailed material lists save time at the lumberyard. These lists help compare suppliers and reduce waste. DIY small wooden house plans often include cut lists and fastener schedules, making planning easier for experienced DIYers.
Kits and prefab options can save on labor costs. While kits may cost more upfront, they save time. Some prefab cabins can be built in days or weeks. Pure plans are the cheapest option but require more tools, time, and DIY skills.
For complex systems, consider hiring a licensed architect or builder. They ensure compliance with codes and obtain necessary permits. For simple projects, an experienced DIYer can follow woodworking house-building plans and complete the job without a contractor.
Compare plans before making a purchase. Look for clear dimensions, revision history, and customer reviews. Affordable small house plans that include both imperial and metric measurements offer flexibility when buying materials in the United States or abroad.
Community forums and designer support can help with the learning process. Buying from designers who offer support often leads to better results than anonymous downloads. This support is crucial when adapting plans to a specific site or local code.
Use a combination of plans, kits, and professional help to fit your budget and skill level. This approach helps avoid surprise costs, keeps timelines realistic, and ensures a safe, durable tiny home.
Real-World Examples and Builder Tips: Rustic Tiny House Plans and Successful Builds
Looking at real projects makes plans come alive. A-Frame weekender cabin plans, small round cabin plans, and portable cabin plans show their worth on actual sites. Builders share photos, cut lists, and timelines, giving a clear idea of what to expect.
Plan catalogues feature a variety of uses. The A-Frame Weekender is a cozy retreat for weekends. The Small Round Cabin Olivia has curved walls that keep it warm in cold weather. The Portable Cabin Lucas is designed to move to different places.
Using prefab parts speeds up construction. Builders can assemble a three-person team in under three hours. Other projects finish in less than a month with a team following detailed plans and using pre-cut panels.
Experienced builders emphasize planning and material lists. Having a clear bill of materials avoids delays and extra trips. Designer support and forums help spot errors early. Local advice is key for adapting plans to your area and climate.
Adapting designs for everyday use is crucial. Count pre-cut pieces and check kerf depths for parts that fit together. Reinforce roofs with internal logs for snow load. Make doors and stairs bigger for better mobility and access.
Using local materials is wise when original materials are hard to find. If slate roofing is not available, choose a local metal or composite roof. This works well for cabins going to different climates.
Here’s a quick comparison of example projects, build times, and adaptation tips. This helps match a plan to your site and schedule.
| Model | Primary Use | Typical Build Time | Adaptation Tip |
|---|---|---|---|
| A-Frame Weekender | Weekend retreat | 1–4 weeks with prefab panels | Raise roof ties for larger loft headroom |
| Small Round Cabin Olivia | Off-grid cozy dwelling | 2–6 weeks using kit parts | Pre-cut curved studs and check kerf fits |
| Portable Cabin Lucas | Transportable living unit | Days to weeks, depending on finish | Verify trailer specs and door clearances |
| Elevated Beach Cottage Eva | Coastal weekend home | 2–8 weeks with local crew | Use corrosion-resistant fasteners and raised foundation |
| Transportable House Plans Samuel | Movable tiny home | Use corrosion-resistant fasteners and a raised foundation | Choose lightweight finishes to meet transport limits |
Ready to Build Your Dream Wooden House?
Don’t waste time searching for incomplete or confusing plans. Get instant access to 16,000+ step-by-step woodworking blueprints that make building easy—even for beginners.
👉 Unlock Ted’s Woodworking Plans Now and start your next project today!
💡 Why DIY Builders Love Ted’s Woodworking:
- ✅ 16,000+ Ready-to-Build Projects – From small homes to furniture and garden sheds
- 🧰 Beginner-Friendly, Pro-Level Results – Clear, detailed, step-by-step instructions
- 📐 Exact Material & Cutting Lists – No waste, no guesswork, no overspending
- 🪚 Lifetime Access + Monthly New Plans – Never run out of inspiration
- 🎁 Bonus Training & Videos – 150+ tutorials, CAD plan viewer, and business guide included
- 💸 One-Time Price ($67) – No monthly fees, no surprises
- 🔁 60-Day Money-Back Guarantee – Risk-free satisfaction promise
Conclusion
Small wooden house plans diy make building a home easy for hobbyists and first-time buyers. These plans range from simple PDFs to detailed sets for professionals. They include both metric and imperial measurements and a list of materials to help with planning and shopping.
Choosing plans from experienced architects and builders adds trust and style. These plans often show pre-cut parts, numbered steps, and precise roof angles. This makes building faster and reduces mistakes. They also include stages for finishing, like doors and staining, for a beautiful and lasting result.
To start, follow a 7-step guide and think about prefab options for quick builds. For systems that need to follow local codes, use professional plans or get help from a contractor. With the right plans and careful work, you can build a cozy cabin, a backyard studio, or a tiny home that lasts.
FAQ
What types of small wooden house plans are available, and which suit my project?
You can find plans for A-frames, rustic log cabins, small round cabins, and more. Choose based on your needs, like a weekend getaway or a full-time home. Consider the site and local rules too. For simple builds, A-Frame and bunkie plans are good. Rustic looks? Go for small wooden cabin designs. Professional plans offer many options to fit your site and budget.
How much do tiny house plans cost, and what do they include?
Prices range from $129 to $490. You get detailed plans, like the Backyard Studio Kenzo and Small Round Cabin Olivia. They include measurements, foundation choices, and materials lists. Higher tiers might add extra help or prefab guides. This makes building easier.
Can I build one of these small wooden houses myself, or do I need professionals?
DIY is possible with good plans, like those for structures on skids. Plans from experienced builders help avoid mistakes. For complex work, hire a pro. Always check local codes and consider hiring an architect or builder for tricky projects.
What is a practical 7-step roadmap to build a small wooden house?
Start with the foundation and site setup. Then, frame the walls and roof. Next, add roof sheathing and waterproofing.Finish with exterior cladding, interior rough-ins, and interior finishes. End with a final inspection and details.
What foundation types do plans support, and how does the choice affect permitting?
You can choose from skids, piers, raised foundations, and slabs. Skids might avoid permits in some places. But local rules vary. Choose based on your needs and local codes. Plans usually offer options for each foundation type.
What common pitfalls should I avoid during construction?
Watch out for wrong cuts, misaligned joints, and poor roof bracing. Also, ensure moisture control and use the right fasteners. Use plans with pre-cut parts or prefab options. For doubts, consult the plan author or a pro.
What materials, tools, and budget tips are recommended for DIY builds?
The plans list all the materials you need. You’ll need basic tools like a saw and a drill. Buy materials wisely to save money. Consider reclaimed materials for savings. Compare plan prices to find the best deal.
How do roof assembly and angle cuts work for small wooden houses?
Plans often require precisely angled cuts for rafters. Use a jig for accurate cuts. Add sheathing, underlayment, and flashing next. Finish with the right roofing for your climate. This ensures a strong and weather-tight roof.
Are off-grid designs and energy-efficiency options available?
Yes, many plans offer off-grid options. Look for insulation, passive solar, and systems integration. These features save energy and money. Professional plans provide detailed notes and lists for efficient systems.
How do prefab kits compare to buying plans only?
Plans are cheaper but require more effort. Prefab kits cost more but save time. They reduce errors and speed up construction. Choose based on your budget and building skills.
Can lofts and porches be included without increasing the footprint much?
Yes, lofts and porches can be added without expanding the house. They increase living space and outdoor areas. Plans provide structural details for these features.
Where can I buy reliable tiny house plans and what should I look for?
Buy from trusted sources with clear prices and experience. Look for detailed plans, materials lists, and step-by-step guides. Plans from experienced builders offer better guidance.
How do I adapt a published blueprint to site-specific needs or mobility requirements?
Adapt plans by changing foundations, roof overhangs, and door placements. Keep structural loads and local codes in mind. Use plans with variant options or consult the designer for modifications.
What finishing options are recommended for durability and aesthetics?
Choose from stained or painted siding, rustic log cladding, and metal roofs. For the inside, use hardwood flooring and trim. Model examples suggest walnut stain and slate roofing. Choose finishes based on climate, maintenance, and budget. Use quality materials for a long-lasting finish.